-
- Contact Us
SBH11-PBPC-D07-ST-BK: Live Specs, Stock & Pricing Update
As of a December 2025 snapshot across major US distributors, listings for SBH11-PBPC-D07-ST-BK show mixed availability and notable price variance — some sellers report items "in stock" with same-day shipping while others report backorders or "out of stock." This update consolidates technical specifications drawn from the manufacturer datasheet and major distributor listings (Digikey, Future Electronics, Octopart) and pairs those specs with real-time stock signals and pricing patterns so engineers and buyers can make an informed sourcing decision quickly. The report uses hands-on interpretation of inventory badges and distributor timestamps to translate what "availability" and lead-time messages mean operationally for US procurement teams.
1 — Product Background & Live Technical Snapshot (background)
Key specifications at a glance
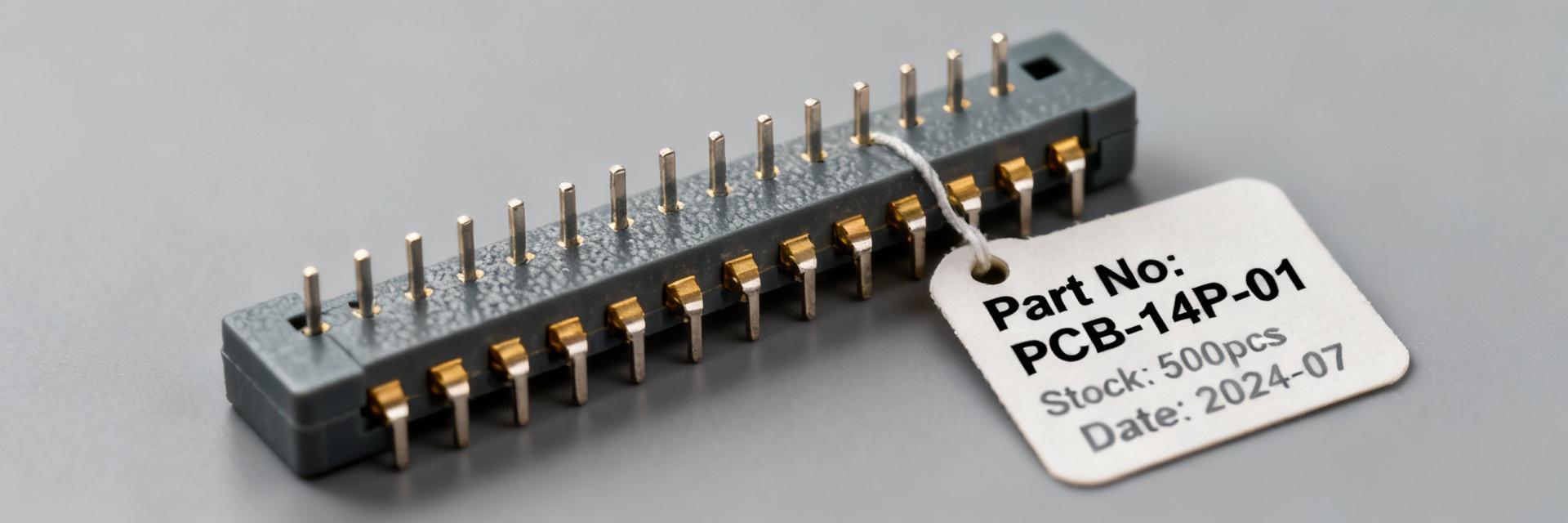
Point: Core connector parameters matter for footprint, signal reliability, and assembly cost. Evidence: Sullins family documentation and distributor listings consistently describe a 14-position, dual-row, 2.54 mm (0.100") pitch through-hole male box header with nickel/gold flash plating and a nylon housing rated for -40°C to +105°C. Explanation: These characteristics make the part suitable for general-purpose board-to-board or cable mating in commercial and many industrial applications; the 2.54 mm pitch simplifies replacement with common headers, while the gold flash finish improves mating corrosion resistance but is less robust than thicker gold plating for extreme-cycle applications. For layout, designers should confirm center-to-center spacing, overall shroud height, and pin protrusion dimensions against the board profile noted in the manufacturer’s datasheet, referenced through distributor part pages.
Datasheet highlights and critical tolerances
Point: Process and dimensional limits dictate assembly choices. Evidence: Datasheet entries from the manufacturer indicate maximum processing temperatures for soldering operations, recommended solder fillet profiles, pin base material (phosphor bronze or brass variants commonly used in this family), and plating notes indicating gold flash over nickel. Explanation: For PCB layout and assembly, critical tolerances include hole size tolerance for through-hole pins, recommended solder reflow profiles if wave soldered, and the seating plane for the shroud. These tolerances influence whether a part will withstand lead-free assembly processes and what through-hole annular ring sizes are required. Engineers should compare the datasheet’s mechanical drawings and critical dimension callouts to their CAD footprint before committing to a BOM line item to avoid re-spins or solderability issues.
Compliance & reliability notes for US designs
Point: Compliance markings and environmental ratings affect qualification in regulated or industrial systems. Evidence: Manufacturer datasheets and distributor product pages commonly list RoHS/lead-free status and, where applicable, UL flammability ratings for the housing material (for example, Nylon with 94V-0 classification if specified). Explanation: For US market designs, confirm RoHS compliance for commercial assemblies and verify UL 94V-0 or equivalent if the connector may be exposed to flame-risk enclosures; absence of UL rating should prompt an additional materials assessment. Reliability guidance includes derating recommendations in elevated ambient scenarios and assessing tolerance to vibration and mating cycles: if a device will see high mating cycles or harsh environments, consider a connector with thicker hard-gold plating or a latching retention feature to improve lifecycle performance and traceability for audits.
2 — Live Availability: Distributor Stock Snapshot (data analysis)
Current distributor statuses (how to read them)
Point: Inventory tags are not standardized across distributor portals and must be interpreted contextually. Evidence: Across platforms (Digikey, Future Electronics, Octopart, distributor portals), labels such as "in stock," "lead time," "backorder," and "discontinued" are accompanied by timestamps, quantity badges, and sometimes ETA windows. Explanation: "In stock" usually means immediate ship from the distributor’s warehouse but confirm timestamp and available quantity; a same-day timestamp within operational hours implies immediate fulfillment. "Lead time" can indicate the part is sourced from the manufacturer with a quoted replenishment delay; check whether the lead-time is factory lead-time or distributor-procurement lead-time. "Backorder" implies an open order queue and possible allocation. Discontinued alerts require action to qualify alternatives. Best practice: always capture the inventory timestamp and available quantity badge when making a purchase decision to create an auditable procurement snapshot.
Real-time checks & automated monitoring tips
Point: Automated monitoring reduces manual checks and shortens reaction time to stock shifts. Evidence: Sourcing teams successfully use Octopart API feeds, distributor email alerts, and RSS or webhook-based notifications to track SKU status changes and price updates. Explanation: Set up an automated feed that pings on status change and includes the inventory timestamp and lot or batch identifiers where available; pair that with threshold-based alerts (e.g., notify procurement when stock ≤ reorder point). For teams that integrate with PLM or ERP, feed inventory signals into the BOM part record to flag potential shortages. Periodic reconciliation between alerts and live distributor pages verifies feed accuracy and prevents false positives from cached or outdated data.
What to do when availability is mixed
Point: Mixed availability across distributors is a common sourcing condition that requires a deliberate playbook. Evidence: In mixed scenarios for this connector, some authorized sellers show immediate stock while others report multi-week lead times; buyers have historically used split orders, sample buys, and approved alternates to mitigate risk. Explanation: Prioritize purchases from authorized distributors showing confirmed stock with timestamped availability; place split orders with secondary authorized distributors as contingency. Where immediate needs exist, request samples from an in-stock seller and concurrently qualify an equivalent part by cross-checking pinout, pitch, and mechanical tolerances. Document the rationale for split buys, listing authorized seller, quantity, and lead-time to maintain traceability and avoid counterfeit risk.
3 — Pricing Trends & How to Compare Quotes (data analysis)
Typical price drivers for this connector family
Point: Several material and commercial factors drive per-unit pricing in 2.54 mm dual-row headers. Evidence: Cost differentials arise from plating spec (gold flash vs. hard gold), packaging (tray vs. bulk tubes), MOQ pricing, and macro factors such as currency and import fees. Explanation: Gold flash finishes command a premium vs. tin/nickel plating due to material cost and processing; packaging in trays suitable for automated assembly typically raises unit cost compared to bulk supply. MOQ and order quantity influence per-unit pricing strongly—higher volumes unlock deeper breaks. Additionally, freight mode, tariffs, and supplier inventory levels can cause price variance across distributors. Use these levers to understand and negotiate distributor quotes and forecast BOM cost confidently.
How to benchmark distributor quotes
Point: A systematic landed-cost approach yields apples-to-apples comparisons across quotes. Evidence: The recommended checklist includes unit price, packaging, freight, taxes, expected lead time, and any ancillary fees; landed-cost calculators or ERP costing modules are commonly used to normalize quotes. Explanation: Step-by-step: 1) Capture the unit price and packaging type (tray, strip, bulk). 2) Add freight options and estimated duties/taxes for import scenarios. 3) Calculate landed cost per unit at target quantity, including potential rework or sample costs. 4) Request volume pricing and turnaround time (TAT) from authorized distributors for exact breaks. This approach reveals the true SBH11-PBPC-D07-ST-BK pricing impact on product cost and supports confident sourcing decisions.
Negotiation levers & cost-saving tactics
Point: Several operational tactics can reduce per-unit landed cost without compromising traceability. Evidence: Consolidated buys, TAP/consignment agreements, accepting alternate packaging, and qualifying approved equivalent parts are frequently used levers. Explanation: Consolidate orders across SKUs to meet MOQ thresholds and reduce freight per unit. Negotiate consignment or TAP arrangements for recurring programs to reduce working capital burden. Ask authorized distributors for alternate packaging options or lower-cost plating options if application allows. Time purchases to supplier promotions or end-of-quarter inventory reductions. Document any approved equivalent parts and maintain traceability records to satisfy audits while lowering procurement costs.
4 — Sourcing Workflow & Alternative Parts (method guide)
How to qualify functional equivalents
Point: Qualification requires mechanical, electrical, and process parity checks. Evidence: Common equivalency criteria include matching pin count and layout, identical 2.54 mm pitch and footprint, equivalent plating and base metal, mechanical retention features, and temperature rating. Explanation: Use a short validation checklist for BOM swaps: 1) Pin mapping and mechanical fit-to-board; 2) Plating and corrosion resistance; 3) Temperature and current handling; 4) Mating compatibility and retention; 5) Manufacturer traceability and authorized distributor availability. For PCB re-spins, compare 2D/3D CAD models and run a DFM check. For high-reliability applications, conduct a short qualification test (mating cycles, thermal cycling) before full substitution.
Short-term workarounds: adapters and substitutes
Point: Temporary substitutes allow production continuity while long-term sourcing is resolved. Evidence: Practical short-term options include compatible Sullins-series equivalents, generic dual-row 2.54 mm headers with similar shroud geometry, or simple adapter PCBs to bridge mating incompatibilities. Explanation: When using substitutes, validate mechanical clearance and signal integrity for critical nets. An adapter PCB can translate a slightly different footprint to the original board without re-spin. For analog or high-speed signals, perform a quick signal-integrity check to confirm impedance and crosstalk remain acceptable. Always document the substitute and conditions under which it is used, then schedule a permanent resolution in the BOM lifecycle plan.
Procurement playbook for US teams
Point: A compact, repeatable procurement sequence reduces lead-time risk. Evidence: Proven five-step sequences used by US procurement teams include verify specification → check three distributors → request samples/lead-time → compare landed cost → place order with contingency supplier. Explanation: Execute the playbook as follows: 1) Confirm the exact part specification against the datasheet and CAD footprint; 2) Check three authorized distributors for stock, timestamp, and price; 3) Request samples or small-quantity buys to validate fit and solderability; 4) Use landed-cost comparison to choose optimal supplier; 5) Place the order, ensure a contingency supplier is on file, and log lot, date, and price in the BOM. This sequence provides auditable decisions and rapid mitigation of shortages.
5 — Distributor Case Notes & Quick Buy Guide (case/display + action)
Authorized distributors to prioritize
Point: Prioritizing authorized distributors reduces counterfeit and traceability risk. Evidence: US-authorized distributors typically include major franchised sellers known for reliable lead times, return policies, and traceability — for this family, listings on large national distributors and recognized regional partners are the preferred sources. Explanation: Verify authorization by checking distributor accreditation statements on their product pages and by requesting manufacturer authorization letters if necessary. Prioritize distributors that show clear lot traceability, robust return policies for mis-ships, and dedicated rep support for escalation. When time-critical, a verified authorized distributor with same-day dispatch capability outweighs a slightly lower unit price from an unverified seller.
Quick-buy checklist for same-day or short-lead needs
Point: A compact checklist helps secure urgent buys without oversight gaps. Evidence: Effective checklists confirm stock timestamp, packaging type, minimum order, shipping options, and direct communication with a sales rep for escalation. Explanation: Before ordering for same-day or next-day fulfillment: 1) Confirm the inventory badge timestamp and quantity; 2) Confirm packaging (tray vs. bulk) to ensure assembly compatibility; 3) Check minimum order quantities and whether additional handling fees apply; 4) Choose expedited shipping with a reliable carrier and verify cut-off times; 5) Contact the distributor rep to confirm pick/pack details and request an order confirmation email to create an audit trail.
Documenting the decision: audit trail & BOM updates
Point: Recording procurement decisions prevents downstream confusion and simplifies audits. Evidence: Best practice logs include part number, lot number, distributor, purchase date, unit price, lead-time, and any approved alternates with justification. Explanation: For each procurement action, capture the distributor page screenshot with timestamp, the PO number, lot or batch identifiers where provided, and the rationale for selection (price, lead-time, qualification status). Update the BOM and PLM records to reflect the lot, vendor, and any substitute part numbers. This audit trail supports warranty claims, failure analysis, and regulatory checks while preserving institutional knowledge for future sourcing cycles.
Summary
- SBH11-PBPC-D07-ST-BK is a 14-position, dual-row 2.54 mm through-hole header; verify mechanical drawings against your footprint and solder process before committing to a BOM.
- Availability varies across US distributors — always capture inventory timestamps and prioritize authorized sellers with traceability to reduce lead-time and counterfeit risk.
- Compare landed cost (unit, packaging, freight, duties) and use consolidated buys or consignment to reduce per-unit pricing impact while maintaining supply continuity.
Frequently Asked Questions — Procurement & Technical
What are the most important SBH11-PBPC-D07-ST-BK technical specifications to confirm before purchase?
Confirm pitch (2.54 mm / 0.100"), position count (14), shroud and height dimensions against PCB stack-up, plating type (gold flash vs. hard gold), base metal, and the operating temperature range. Verify datasheet soldering/process limits and hole size tolerances for through-hole pins. These checks prevent footprint mismatches, solderability problems, and lifecycle shortfalls.
How should a US buyer interpret "in stock" vs "lead time" on distributor pages for this connector?
"In stock" typically means immediate fulfillment from that distributor’s inventory but always confirm the timestamp and the available quantity; "lead time" indicates the distributor will procure from the manufacturer or a supplier and provides an ETA—clarify whether the lead time is factory or distributor procurement lead time. When possible, ask for a specific ship date and confirm via the distributor sales rep to avoid surprises.
What quick steps reduce cost when pricing and ordering this connector family?
Benchmark quotes on a landed-cost basis (unit price + packaging + freight + duties), negotiate volume breaks, consolidate orders to meet MOQ thresholds, consider alternate packaging for cost savings, and request TAP/consignment arrangements for ongoing programs. Always document any approved alternates and maintain authorization records to satisfy procurement audits.
- Technical Features of PMIC DC-DC Switching Regulator TPS54202DDCR
- STM32F030K6T6: A High-Performance Core Component for Embedded Systems
- Tamura L34S1T2D15 Datasheet Breakdown: Key Specs & Limits
- PAL6055.700HLT Datasheet: Complete Technical Report
- FDP027N08B MOSFET Datasheet Deep-Dive: Key Specs & Test Data
- LT1074IT7: Complete Specs & Key Parameters Breakdown
- How to Verify G88MP061028 Datasheet and Specs - Checklist
- NFAQ0860L36T Datasheet: Measured IPM Performance Report
- 90T03P MOSFET: Complete Specs, Pinout & Ratings Digest
- 3386F-1-101LF Datasheet & Specs — Pinout, Ratings, Sources
-
 MM74HC4050NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BUFFER NON-INVERT 6V 16DIP
MM74HC4050NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BUFFER NON-INVERT 6V 16DIP -
 MM74HC4049NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BUFFER NON-INVERT 6V 16DIP
MM74HC4049NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BUFFER NON-INVERT 6V 16DIP -
 MM74HC4040NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BINARY COUNTER 12-BIT 16DIP
MM74HC4040NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BINARY COUNTER 12-BIT 16DIP -
 MM74HC4020NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BINARY COUNTER 14-BIT 16DIP
MM74HC4020NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BINARY COUNTER 14-BIT 16DIP -
 MM74HC393NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BINARY COUNTR DL 4BIT 14MDIP
MM74HC393NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BINARY COUNTR DL 4BIT 14MDIP -
 MM74HC374NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC FF D-TYPE SNGL 8BIT 20DIP
MM74HC374NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC FF D-TYPE SNGL 8BIT 20DIP -
 MM74HC373NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC D-TYPE TRANSP SGL 8:8 20DIP
MM74HC373NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC D-TYPE TRANSP SGL 8:8 20DIP -
 LT1213CS8Linear Technology (Analog Devices, Inc.)IC OPAMP GP 2 CIRCUIT 8SO
LT1213CS8Linear Technology (Analog Devices, Inc.)IC OPAMP GP 2 CIRCUIT 8SO -
 MM74HC259NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC LATCH ADDRESS 8BIT 16-DIP
MM74HC259NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC LATCH ADDRESS 8BIT 16-DIP -
 MM74HC251NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC MULTIPLEXER 1 X 8:1 16DIP
MM74HC251NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC MULTIPLEXER 1 X 8:1 16DIP