74LVC1G07GW-Q100 Datasheet Deep Dive: Pinout & Key Specs
2026-02-08 10:05:32
0
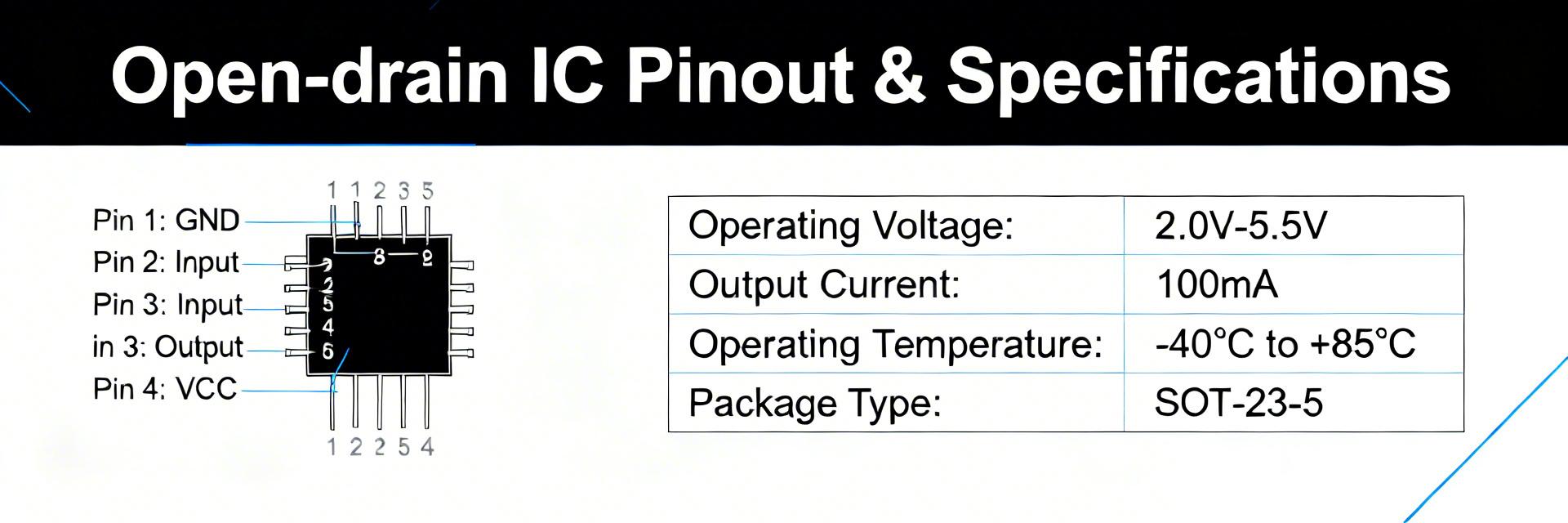
Comprehensive technical analysis of the automotive-grade single non-inverting buffer with open-drain output. The 74LVC1G07GW-Q100 is a single non-inverting buffer with an open-drain output designed for mixed-voltage systems and demanding environments. Key datasheet figures frame its usefulness: wide VCC support from 1.65–5.5 V, very low standby ICC in the microampere range, open-drain output capable of sourcing external pull-ups and sinking up to ~32 mA, and an extended ambient rating down to −40°C and up to +125°C for automotive-grade robustness. This article walks through the 74LVC1G07GW-Q100 datasheet to explain pinout, electrical characteristics, integration tips, and troubleshooting guidance for practical designs. Readers will get a pin-by-pin description, package and soldering notes, DC and AC parameter interpretation, layout and pull-up resistor guidance, thermal and qualification considerations, plus a compact pre-deployment checklist. The aim is practical application: selecting pull-ups and decoupling, estimating timing with given propagation delays and capacitive loads, and avoiding common pitfalls when the part is used as a level-shifting open-drain buffer on shared buses. Background & Device Overview Core Functionality The part is a single non-inverting buffer with an open-drain output used to gate and isolate logic signals. The open-drain topology means the device actively pulls the line low but relies on an external pull-up for a defined high level. This enables wire-OR logic, level translation between different VCC domains, and shared-bus operation. Key Selling Points The datasheet highlights low-voltage operation, broad VCC range, and automotive-level qualification. Typical ICC in standby is in the microampere class, and IO sink capability approaches several tens of milliamps. Q100-style qualification implies extra screening and extended-temperature robustness. Pinout & Package Details Pin-by-Pin Description The five-pin package pin mapping is straightforward: VCC, GND, input (A), output (Y open-drain), and any NC or substrate ties as specified. For documentation and PCB silkscreen, ensure the orientation notch is clearly identified to prevent assembly errors. Pin Number Symbol Description 1 A Data Input 2 GND Ground (0 V) 3 NC / n.c. Not Connected 4 Y Open-Drain Output 5 VCC Supply Voltage Electrical Characteristics: DC and AC Specs Operating Voltage Visualization (VCC) 1.65V - 5.5V Range 0V 10V Before selection, verify supply range, absolute-max ratings, logic thresholds, and leakage. Operating VCC is 1.65–5.5 V; absolute max VCC and thermal limits must be respected. When using pull-ups, remember the added RC time constant from the resistor and bus capacitance slows edges; select pull-ups to balance required edge speed and static current. Integration & Design Recommendations ⚡ Power & Layout • Use a 0.1 μF ceramic decoupling capacitor close to the VCC pin. • Keep input and output traces as short as possible. • Route sensitive lines away from high-current traces. 🔗 Pull-up Selection Pull-ups define high-level voltage and edge speed. Use R = (VCC − VOL_max)/I_pull as a guide. Typical Values: • 10 kΩ – 100 kΩ: Low power, static logic • 2.2 kΩ – 10 kΩ: High speed (3.3V/5V) Thermal & Automotive Reliability Calculate power dissipation (Pd = ICC*VCC + Iout*Vdrop) to assess thermal margin. For automotive applications, the Q100-style qualification implies additional screening and suitability for extended temperature ranges. Account for extended temp drift in thresholds and possibly tighter derating for long-life reliability in harsh environments. Testing & Troubleshooting Checklist Common Issues ❌ No output (Missing pull-up) ❌ Slow edges (High bus capacitance) ❌ High current (IO limit exceeded) Pre-Deployment Checklist ✅ Verify pin 1 orientation ✅ Confirm VCC is 1.65V-5.5V ✅ Validate pull-up resistor value Summary The 74LVC1G07GW-Q100 is a compact open-drain single buffer ideal for level translation, shared-bus designs, and low-power systems where small packages and automotive-grade robustness are required. Critical items to watch are the VCC operating range, correct pull-up strategy, and the IO sink limits under worst-case scenarios. For integration, prioritize local decoupling, short trace runs, and calculated pull-up choices that balance rise time against static current. Consult the manufacturer datasheet for final sign-off and validate with a prototype run before volume release. Open-Drain Logic AEC-Q100 Qualified 1.65V - 5.5V Common Questions (FAQ) What are the key limits listed in the 74LVC1G07GW-Q100 datasheet? + The datasheet lists the operating VCC range (1.65–5.5 V), absolute maximum ratings, typical standby ICC in microamperes, IO sink capability up to roughly 32 mA, VIH/VIL thresholds, and propagation delays under specified loads. Use those figures to verify logic compatibility and thermal margins. How do I choose the right pull-up resistor? + Select R so that R = (VCC − VOL_max) / I_pull where I_pull is the desired sink current. For 3.3 V buses, 2.2 kΩ–10 kΩ balances speed and power; for 5 V use lower values for faster edges. Account for bus capacitance when finalizing the value. What are the fastest troubleshooting steps if the output is inactive? + First verify VCC and GND are present, confirm a pull-up resistor is installed and connected, probe the input for valid thresholds, and inspect for soldering errors. If edges are slow, reduce the pull-up resistance or check for excessive bus capacitance.
READ MORE
 MM74HC4050NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BUFFER NON-INVERT 6V 16DIP
MM74HC4050NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BUFFER NON-INVERT 6V 16DIP MM74HC4049NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BUFFER NON-INVERT 6V 16DIP
MM74HC4049NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BUFFER NON-INVERT 6V 16DIP MM74HC4040NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BINARY COUNTER 12-BIT 16DIP
MM74HC4040NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BINARY COUNTER 12-BIT 16DIP MM74HC4020NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BINARY COUNTER 14-BIT 16DIP
MM74HC4020NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BINARY COUNTER 14-BIT 16DIP MM74HC393NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BINARY COUNTR DL 4BIT 14MDIP
MM74HC393NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BINARY COUNTR DL 4BIT 14MDIP MM74HC374NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC FF D-TYPE SNGL 8BIT 20DIP
MM74HC374NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC FF D-TYPE SNGL 8BIT 20DIP MM74HC373NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC D-TYPE TRANSP SGL 8:8 20DIP
MM74HC373NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC D-TYPE TRANSP SGL 8:8 20DIP LT1213CS8Linear Technology (Analog Devices, Inc.)IC OPAMP GP 2 CIRCUIT 8SO
LT1213CS8Linear Technology (Analog Devices, Inc.)IC OPAMP GP 2 CIRCUIT 8SO MM74HC259NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC LATCH ADDRESS 8BIT 16-DIP
MM74HC259NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC LATCH ADDRESS 8BIT 16-DIP MM74HC251NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC MULTIPLEXER 1 X 8:1 16DIP
MM74HC251NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC MULTIPLEXER 1 X 8:1 16DIP