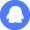
-
- Contact Us
Amphenol 91921-31111LF: Complete Specs & Ratings
Data-driven hook: Rated for 500 V and an operating range from −55 °C to +125 °C, the Amphenol 91921-31111LF is a compact 11-position, 1.00 mm pitch board‑to‑board vertical SMD receptacle used widely in industrial and consumer electronics for reliable mezzanine connections. This reference synthesizes key points from the official datasheet and distributor specs to give engineers, purchasers, and PCB designers an actionable summary of electrical limits, mechanical footprint guidance, assembly practices, and sourcing notes for quick decision-making.
1 — Background: product overview & key uses (background)
What it is — form factor & family
Point: The part is a vertical surface‑mount board‑to‑board receptacle with 11 positions at 1.00 mm pitch; it belongs to the Conan®/Amphenol compact mezzanine family and is optimized for space‑constrained mezzanine stacking. Evidence: Manufacturer documentation and product listings identify the component as an 11‑position, 1.00 mm pitch vertical receptacle offered in tape‑and‑reel packaging and commonly suffix‑coded with LF for lead‑free termination. Explanation: For PCB designers this means a small footprint with standardized mechanical mating to Conan® headers; tape-and-reel packaging supports automated placement, and the LF suffix indicates RoHS‑compliant, lead‑free finish options suitable for modern SMT assembly flows.
Target markets & typical applications
Point: The connector targets markets requiring dense, reliable mezzanine connections, including industrial control, telecom modules, instrumentation, and handheld electronics. Evidence: Application notes and distributor usage examples show the Conan® 1.00 mm family in stacked module solutions where board height, signal integrity, and repeatable mating cycles matter. Explanation: Designers choose the 1.00 mm Conan® series for its balance of density and mechanical robustness — it supports multi‑board assemblies (mezzanine modules, daughtercards) where low profile and reliable contacts are essential for vibration and field use.
Where to find the official datasheet & manufacturer notes
Point: The authoritative technical detail resides in the Conan® 1.00 mm system datasheet and the Amphenol product page, with distributor pages (Mouser, Digi‑Key) useful for cross‑checking stock and spec callouts. Evidence: Amphenol’s Conan® datasheet and part product page list the dimensional drawings, materials, and test limits; distributor spec pages repeat electrical/mechanical callouts and show packaging SKUs. Explanation: For final acceptance and sign‑off always refer to the official datasheet for tolerances and test procedures; use distributor pages to confirm availability, packaging unit (tape & reel), and any stock/lead‑time flags prior to BOM freeze.
2 — Datasheet at a glance: electrical & plating specs (data analysis)
Electrical ratings & limits
Point: Key electrical ratings include a 500 V rated voltage and specified operating temperature limits; other electrical limits (current rating, insulation resistance, dielectric withstanding voltage, contact resistance) must be validated from the datasheet for final designs. Evidence: The Amphenol product listing and Conan® datasheet call out 500 V as the rated voltage and provide test methods for contact resistance and dielectric testing; distributor specs mirror these entries. Explanation: In practice, designers should use the datasheet’s test methods (e.g., specified measurement conditions for contact resistance and dielectric withstanding voltage) when performing acceptance testing. Where the datasheet does not publish continuous current for a specific position count, conservative derating per trace and thermal models is recommended and thermal/power limits should be validated on the target PCB assembly prior to production.
| Parameter | Value / Note |
|---|---|
| Rated voltage | 500 V |
| Operating temperature | −55 °C to +125 °C |
| Contact resistance | See manufacturer datasheet test conditions (measure per datasheet) |
| Insulation resistance | See datasheet (use specified test voltage) |
| Dielectric withstanding | See datasheet/test spec for method and voltage level |
Contact materials & plating options
Point: Contacts use a base metal with selectable plating (gold and GXT™ options are cited) and measured plating thicknesses where listed (for example representative listings include 15 µin / 0.38 µm gold). Evidence: Manufacturer and distributor spec pages list plating finish options and typical plating thicknesses used in the Conan® family. Explanation: Plating choice impacts solderability, insertion loss, contact resistance, and mating life: gold offers low resistance and corrosion resistance for frequent mating, while selective plating (GXT™ or tin where specified) can reduce cost for low‑cycle use. Confirm the exact finish on the order due to multiple finish variants across distributors.
Environmental & reliability ratings
Point: Environmental and reliability characteristics include the −55 °C to +125 °C range, specified mating cycles, and standard mechanical test ratings for vibration and shock in the datasheet. Evidence: The Conan® datasheet and product notes specify temperature ranges and recommend test methods for durability/mating cycles; distributor pages often echo mating cycle counts and RoHS/REACH compliance. Explanation: For regulated or harsh‑environment deployments, request manufacturer qualification documentation; design margins should account for thermal cycling, humidity, and vibration per the device’s stated ratings and intended field profile.
3 — Mechanical & footprint details: dimensions, pitch, footprint (data analysis)
Critical dimensions & drawing callouts
Point: The connector’s fundamental geometry centers on the 1.00 mm pitch and 11 position array; key overall depth and height dimensions are provided on the Conan® mechanical drawing and must be used for PCB keep‑out and stacking clearance. Evidence: Datasheet drawings give exact PCB cutouts, overall height (example listings indicate depths in the ~5.5 mm range for comparable parts), and pin pitch tolerances. Explanation: Use the manufacturer’s annotated dimension tables when creating CAD footprints — copying approximate or rounded values can cause mating interference or insufficient solder fillet clearance; always align the component centerline and courtyard per the vendor drawing.
| Dimension | Typical value / note |
|---|---|
| Pitch | 1.00 mm |
| Positions | 11 |
| Overall depth / mate space | Confirm on datasheet drawing (manufacturer drawing recommended) |
| Board retention | SMD pads with retention features; follow vendor land pattern |
PCB mounting, solder retention & recommended land pattern
Point: The part is intended for SMD assembly with a recommended land pattern and solder fillet geometry supplied by Amphenol; following the recommended stencil and pad sizes yields reliable solder joints and retention. Evidence: Manufacturer drawing and footprint notes specify pad dimensions, courtyard, and solder fillet expectations; distributor CAD downloads often provide reference land patterns. Explanation: For best yield, import vendor CAD footprint, follow pad-to-pad clearances, apply recommended solder mask openings, and validate stencil aperture percentages for the SMD tails. If mechanical retention is required in high‑shock assemblies, add anchors or glue per the assembly guidance.
Mating geometry & stacking/height options
Point: Mate orientation is vertical; mating headers/plug counterparts in the Conan® family match the 1.00 mm pitch and are offered in multiple stack heights to suit board‑to‑board separation. Evidence: Part family documentation lists compatible headers and typical stack heights; tolerances and mechanical locking features are shown on mating drawings. Explanation: When choosing stack height, account for component clearances on both boards and tolerance stack‑up; include guide posts or pin alignment features in tight‑tolerance stacks to reduce insertion misalignment and contact wear.
4 — Assembly, testing & reliability guidance (method guide)
Reflow & soldering recommendations
Point: Reflow profiles should follow the solder paste and board assembly guidelines, and the part’s datasheet reflow recommendations where provided; LF (lead‑free) parts require lead‑free thermal profiles. Evidence: Amphenol guidance and standard SMT practice call for peak reflow temperatures compatible with lead‑free alloys and for moisture sensitivity handling if applicable. Explanation: Use the manufacturer’s recommended peak temperature and time‑above‑liquidus ranges for lead‑free assembly; if the component has a moisture sensitivity level, pre‑bake per the datasheet before assembly to avoid popcorning. When in doubt, consult your paste vendor and run a DOE with representative PCBs.
Handling, inspection & test procedures
Point: ESD precautions, visual/X‑ray inspection of solder fillets, and dedicated tests for contact continuity and retention force are standard acceptance steps. Evidence: Datasheet test methods and distributor test callouts define how contact resistance and retention force are measured; production test plans typically include continuity checks and sample pull tests. Explanation: Create an inspection checklist that includes correct orientation, solder fillet quality on SMD tails, no bridging, and mechanical seating. For incoming inspection, validate sample parts for mating fit with a representative header and measure contact resistance per the datasheet method before lot acceptance.
Reliability best practices in design
Point: To improve field reliability, designers should consider PCB reinforcement, strain relief, derating, and supplemental mechanical anchoring in high‑shock environments. Evidence: Field reports and application notes for mezzanine connectors recommend glue or mechanical anchors and conservative derating when thermal dissipation is limited. Explanation: Use fillet support under the connector where possible, avoid placing heavy components directly on stacked assemblies, and include mechanical fasteners or standoffs to transfer shock loads away from solder joints. Implement accelerated thermal/vibration testing during qualification to catch assembly weaknesses early.
5 — Cross-references, substitutes & sourcing (case study / market)
Common alternates & family variants
Point: Within the Conan® family there are many pitch/position variants and related series (e.g., other 1.00 mm position counts or adjacent series numbers); differences to track include pitch, plating, and stack height. Evidence: Cross‑reference comparisons from distributor pages show near equivalents (other 9192x/9193x catalog numbers) with slight mechanical or finish differences. Explanation: When choosing a substitute, confirm pitch and mechanical mate compatibility first, then plating and mating cycles; avoid substitutes that alter mating geometry or keying unless the mate counterpart is also changed.
Distributor availability & ordering examples
Point: Major distributors list the part with manufacturer part number and packaging details (tape & reel); confirm SKU, finish, and MOQ on the distributor page before ordering. Evidence: Distributor entries commonly indicate packaging quantity, lead times, and manufacturer finish codes in the item description. Explanation: For BOM entries, specify full manufacturer part number with suffix (finish/packaging) and include approved alternates to reduce lead‑time risk. When ordering high volumes, request manufacturer lead‑time and consider safety stock for long‑lead parts.
Compliance & qualification notes for procurement
Point: Confirm RoHS and REACH compliance and ask for manufacturer qualification/test reports for regulated markets. Evidence: Product listings typically include RoHS/REACH flags and may reference qualification standards. Explanation: Procurement should request certificates of conformity and any lot‑specific test reports for regulated or safety‑critical programs; retain these documents in the supplier approvals package.
6 — Practical design & procurement checklist (action guide)
Quick-design checklist for CAD/PCB engineers
Point: Before layout, verify footprint match, mating connector availability, mechanical clearances, and thermal/current considerations. Evidence: The manufacturer footprint and recommended land pattern provide pad sizes and courtyard; distributor CAD files and datasheet drawings are the canonical references. Explanation: Pre‑layout tasks: import vendor footprint, confirm component keep‑outs for stacked modules, verify board thickness and standoff clearances, and ensure power traces are derated by thermal modeling. Add mechanical anchors or glue if the product will see shock/vibration.
BOM & manufacturing checklist for purchasers
Point: Include full part number template, suffix options for finish (LF, plating code), and packaging code on every PO; list approved alternates to avoid single‑source shortages. Evidence: Distributor pages show suffix variations and packaging codes; procurement templates should capture finish and packaging explicitly. Explanation: RFQ items should specify the exact manufacturer P/N including LF suffix, required finish, tape‑and‑reel quantity, and acceptable alternates; maintain a safety stock recommendation based on lead time and production ramp.
Troubleshooting & field-failure triage
Point: Common failure modes include solder joint cracks and contact wear; initial diagnostics should be visual inspection, continuity measurement, and mechanical mate testing. Evidence: Field reports and repair logs for board‑to‑board assemblies commonly cite solder fatigue and contamination as root causes. Explanation: For failures, inspect solder fillets for voids/cracks, measure contact resistance relative to baseline, and perform a simple mechanical retention and mating cycle test to determine if the fault is assembly, design, or wear related.
Summary
Concise recap: The Amphenol 91921-31111LF is a compact 11‑position, 1.00 mm pitch vertical SMD board‑to‑board receptacle with a 500 V rating and −55 °C to +125 °C operating range; consult the datasheet for definitive electrical, mechanical, and assembly specifications and follow the checklists above to ensure correct PCB footprint, procurement accuracy, and reliability validation.
Key summary
- Rated 500 V and −55 °C to +125 °C — verify thermal margins and derating in your assembly.
- 1.00 mm pitch, 11 positions — import vendor PCB footprint and follow crease pad/stencil guidance.
- Confirm plating and finish (gold/GXT options) on the order — finish affects contact life and solderability.
- Use distributor pages and the Conan® datasheet for exact test methods, mating cycles, and tolerance callouts.
FAQ
Is 91921-31111LF rated for high voltage applications?
The part is specified with a rated voltage of 500 V by the manufacturer; for high voltage or safety‑critical applications confirm dielectric withstanding voltage and creepage/clearance requirements from the official datasheet and perform application‑specific electrical testing under expected environmental conditions before qualification.
How should I confirm the correct footprint for 91921-31111LF?
Download or transcribe the manufacturer’s recommended land pattern from the Conan® system mechanical drawing and use the distributor CAD files where available; verify pad sizes, courtyard, and recommended stencil apertures, then run a first article assembly to validate solder fillet formation and mechanical seating.
What procurement details should be included on the PO for 91921-31111LF?
Always specify the full manufacturer part number including LF suffix, exact finish/plating code, packaging (tape & reel quantity), and approved alternates. Request certificates of conformity and any required test reports for regulated markets and allow time for lead‑time confirmation from the distributor or manufacturer.
- Technical Features of PMIC DC-DC Switching Regulator TPS54202DDCR
- STM32F030K6T6: A High-Performance Core Component for Embedded Systems
- Tamura L34S1T2D15 Datasheet Breakdown: Key Specs & Limits
- PAL6055.700HLT Datasheet: Complete Technical Report
- FDP027N08B MOSFET Datasheet Deep-Dive: Key Specs & Test Data
- LT1074IT7: Complete Specs & Key Parameters Breakdown
- How to Verify G88MP061028 Datasheet and Specs - Checklist
- NFAQ0860L36T Datasheet: Measured IPM Performance Report
- 90T03P MOSFET: Complete Specs, Pinout & Ratings Digest
- 3386F-1-101LF Datasheet & Specs — Pinout, Ratings, Sources
-
 MM74HC4050NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BUFFER NON-INVERT 6V 16DIP
MM74HC4050NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BUFFER NON-INVERT 6V 16DIP -
 MM74HC4049NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BUFFER NON-INVERT 6V 16DIP
MM74HC4049NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BUFFER NON-INVERT 6V 16DIP -
 MM74HC4040NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BINARY COUNTER 12-BIT 16DIP
MM74HC4040NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BINARY COUNTER 12-BIT 16DIP -
 MM74HC4020NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BINARY COUNTER 14-BIT 16DIP
MM74HC4020NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BINARY COUNTER 14-BIT 16DIP -
 MM74HC393NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BINARY COUNTR DL 4BIT 14MDIP
MM74HC393NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC BINARY COUNTR DL 4BIT 14MDIP -
 MM74HC374NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC FF D-TYPE SNGL 8BIT 20DIP
MM74HC374NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC FF D-TYPE SNGL 8BIT 20DIP -
 MM74HC373NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC D-TYPE TRANSP SGL 8:8 20DIP
MM74HC373NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC D-TYPE TRANSP SGL 8:8 20DIP -
 LT1213CS8Linear Technology (Analog Devices, Inc.)IC OPAMP GP 2 CIRCUIT 8SO
LT1213CS8Linear Technology (Analog Devices, Inc.)IC OPAMP GP 2 CIRCUIT 8SO -
 MM74HC259NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC LATCH ADDRESS 8BIT 16-DIP
MM74HC259NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC LATCH ADDRESS 8BIT 16-DIP -
 MM74HC251NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC MULTIPLEXER 1 X 8:1 16DIP
MM74HC251NSanyo Semiconductor/onsemiIC MULTIPLEXER 1 X 8:1 16DIP